
CAR-T
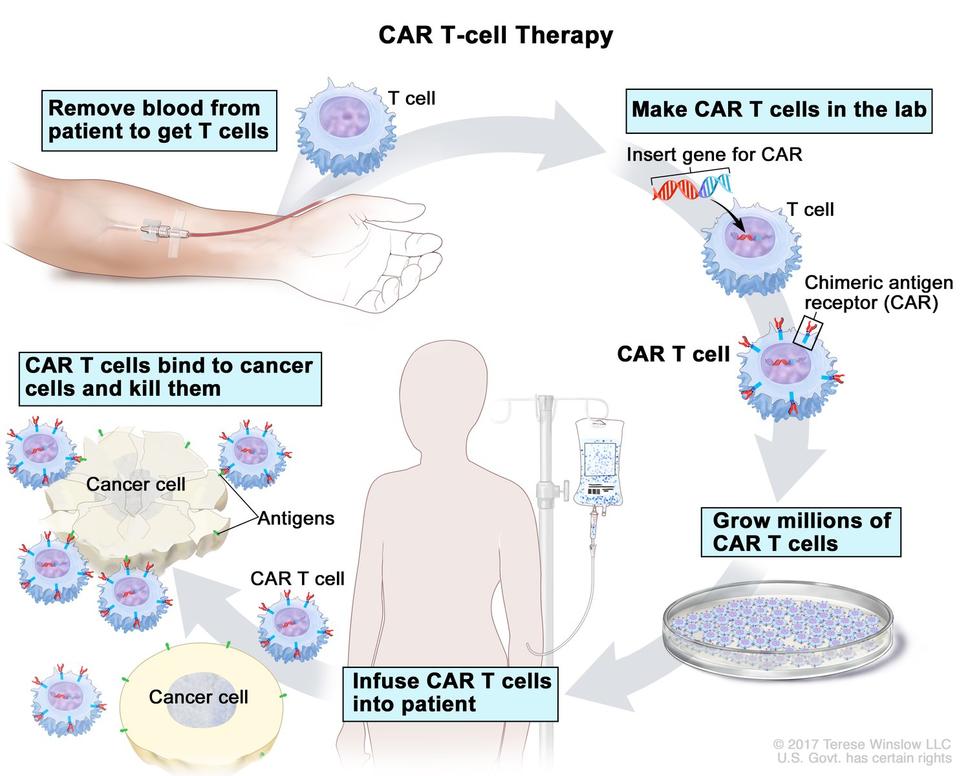
Immunotherapy enhances the power of a patient’s immune system to attack tumors. An immunotherapy approach, called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, uses patients’ own immune cells to treat their cancer
How does CAR T-cell therapy treat leukemia?
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that improves the ability of T-cells to attach to leukemia cells and destroy them. T-cells have proteins called receptors that bind to antigens (another type of protein) on cells that pose a threat. Once attached, the T-cells activate, multiply, and send signals to the immune system to destroy the diseased cells.
Different types of leukemia and other blood cancers have unique antigens. Sometimes, T-cells don’t have the right receptors for a cancer cell antigen. As a result, the T-cells can’t bind to them, and the leukemia cells grow out of control. CAR T-cell therapy changes the T-cells so they can attach to and destroy cancer cells. To determine whether CAR T-cell therapy can help, patients undergo a genetic test (a type of blood test) to identify the cancer’s antigen type.

What resources are available?
Fact Sheets and Guides ›
Education Programs ›
Helpline ›
leukemia Support Network ›

What can I do to help?
Get Involved ›
Find a Walk or Endurance Event ›
Create a Fundraiser ›
Submit a Story of Hope ›
How Does CAR T-cell Therapy Work?
In CAR T-cell therapy for lymphoma, a lab modifies a patient's blood cells to help them fight cancer cells in the blood. Once a patient's blood is drawn, a lab engineers the T-cells to gain a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), which can bind to a protein on the cancer cells. The CAR T-cells are multiplied to produce more engineered T-cells. When there are enough of these special cells, they are reintroduced to the patient via a blood infusion.malignant plasma cells then produce an abnormal antibody called M protein, high levels of which are a hallmark characteristic of multiple myeloma.
Approved CAR T Cell Therapies in leukemia
Approved CAR T Cell therapies include:
| Approved drug | Approved drug indication |
|---|---|
| Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) |
|
| Inaticabtagene Autoleuce(CNCT19) |
CAR T Cell Process
1. Leukapheresis
Your T cells are obtained through a process called leukapheresis, which usually takes three to four hours.
2. T-Cell Engineering
The T cells are sent to a processing center where they are genetically engineered to target your lymphoma.
3. CAR T Cell Transport
Once enough of the CAR-T cells are available at the processing center, the cells are frozen for transport to your certified treatment center.
4. Lymphodepleting Chemotherapy

A few days prior to your CAR-T cell infusion, you will receive low-dose chemotherapy.
5. CAR T Cell Infusion
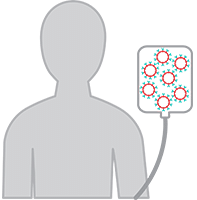
A few days after completing chemotherapy, you will receive your CAR-T cells at your certified treatment center.
6. CAR T Cells Attack the Lymphoma
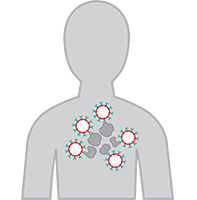
Once the CAR-T cells enter your body, they begin to multiply and attack the lymphoma cells.
Patient Stories
-
**Patient Story: CAR-T Therapy Brings New Hope for Lymphoma Patients – A Case from a Chinese Hospital** In the field of cancer treatment, China has achieved groundbreaking success with CAR-T cell therapy, especially in treating relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Today, we share the story of one patient whose life was transformed through this revolutionary treatment Read More
-
**Patient Story | Chinese CAR-T Therapy: An Inspiring Journey of Changing Fate for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (R/R DLBCL)** #CAR-T #DLBCL #Lymphoma #CARTtherapy #RRDLBCL #Patientstory #CD19 In the field of cancer treatment, China has made remarkable strides in CAR-T cell therapy, especially in the fight against relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL). Read More












